
A SWOT Analysis is a simple but effective tool used to examine an organization’s business prospects determine the strategy that an organization will employ to achieve its goals. It is normally plotted on a simple 2 x 2 matrix. Scroll down for an example.
SWOT stands for:
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Threats
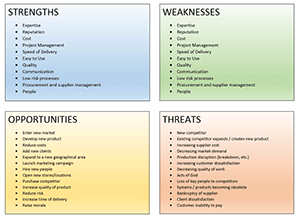
Strengths
This refers to the actions that your organization excels at. The best source of this information is customers or clients, if you are in a position to ask them. But I would suggest you probably have a pretty good idea already. It isn’t usually too hard for most people to see what their organization does better than others.
Here is a quick checklist to help in your brainstorming to find your strengths:
- Good reputation
- Superb after sales service
- Strong technical expertise
- Patents and other intellectual property
- Exceptional sales force
- Strong research and development
- Wide product range
- Access to capital (financing, debt,etc.)
- Strong balance sheet
- High motivation and morale
- Strong management
- Low cost production
- Good relationships with suppliers
Weaknesses
These are the actions your organization does not excel at. Again, the best source is customers or clients, if you are in a position to ask them.
Underperformance in an organization is often ignored or kept quiet, but can be the missing link that causes the company to turn its fortunes around. You can use the same checklist as for strengths, above, to brainstorm for weaknesses.
 Opportunities
Opportunities
Opportunities are the actions the organization could do that are most likely to succeed in achieving the organization’s goals. Opportunities can fall into the categories of:
- Economic: The future market demand for the product or service. Changes in interest rates or currency exchange rates. Future products/services from competitors.
- Technological: An increase in sales due to better technology. Also, a decrease in costs to produce the product, or a better competitive position because of fast rollout of technology.
- Social: Demographics, such as population shifts, and attitudes toward issues such as health and wellness. Irrational market ‘love’ of certain products.
- Political: The tax environment and tariffs. Opportunities from future changes in regulations.
Threats
These are the potential negative effects from factors outside the organization’s control. A strong corporate strategy requires a strong analysis of threats and related action plans. Threats can be classified as internal or external.
- Internal: Employees leaving, equipment breaking down, harmful corporate reorganization, decreasing quality of work, loss of client relationships.
- External: Market demand, increasing supplier costs, systems and processes becoming obsolete, technological factors, acts of God.
SWOT Analysis Template
We have developed a free template [download id=”1825″]. It includes a checklist for the typical types of things you might see in it.





